The percentage of teleworkers has been gradually increasing over the past 20 years in the US. Modern employees demand home-working options but what about teleworking in coworking spaces? How do coworking and teleworking work hand in hand, nowadays, in Europe? We asked Xavier de Mazenod, one of the most famous teleworking and coworking expert in France.
Hi Xavier. Can you introduce yourself as well as Zevillage?

Xavier de Mazenod
Being a former journalist, I created the company Adverbe in 2004: A consulting and training company regarding new forms of work. Since then, we have been publishing the Zevillage website, a site specialized in the transformation of work, organizations and workspaces. We try to convey to companies all the practices and changes we observe.
How would you depict the acceptance of teleworking in France, in 2019, and what still keeps companies from embracing it fully?
Teleworking is an old idea in France that goes back to the 90s. But in reality, it has long progressed underground and informally in companies. Few had formalized it and incorporated it into a human resources strategy.
 For the last 3-4 years, we have witnessed a rapid change. Teleworking has become part of HR policies for quality of work life balance. Perhaps because companies are realizing that millennials are demanding flexibility in the organization of their work and a greater harmony between their personal time and their time at work. This is important for the image of the company, its “employer brand”. We even have testimonials from young candidates refusing job offers from companies that did not set up teleworking.
For the last 3-4 years, we have witnessed a rapid change. Teleworking has become part of HR policies for quality of work life balance. Perhaps because companies are realizing that millennials are demanding flexibility in the organization of their work and a greater harmony between their personal time and their time at work. This is important for the image of the company, its “employer brand”. We even have testimonials from young candidates refusing job offers from companies that did not set up teleworking.
The anti-teleworking blockade is still coming from the same cultural cause as 20 years ago: a presidential view of management, a too hierarchical organization and management methods that rely on control and not on trust.
This is not to blame on managers, they do as they can and as they have learned. It’s just a statement.
For what you know, do you see a wide difference between countries in Europe with respect to the teleworking acceptance rate and practices?
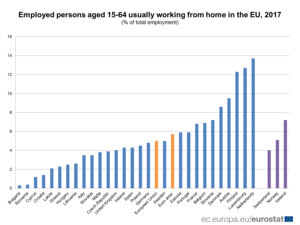
Less than ten years ago, in 2009, there were two distinct blocks: Northern Europe (32.4% of the employed population in Finland, 26.8%, 22.3% in the UK) who already had a high rate of teleworkers, and southern countries (France 8.4%, Italy 5%) at the back of the pack. Since then, France has come back quickly. In fact, teleworking works as a indicator of the degree of trust between managers and employees.
The French utility group EDF announced the creation of internal coworking all over their locations spread out across France. Is this a new step in teleworking policies by French companies, would you say?
I will not say that corpoworking (“Corpoworking” is a word used in France in the corporate world to refer to a coworking model designed for a specific corporate audience which has no equivalent anywhere else) is a mutation of teleworking – but rather a complementary offer. An offer that also reassures companies, since their employees remain in a controlled environment.
Until about 5 years ago, in France, teleworking was practiced in 80 or 90% from home. Since then, employees have greater access to “corpoworking” mainly because professional-level offers have appeared with “industrial” players such as Bouygues Immobilier and Accor or the evolution of former business centers like Regus or the emergence of operators like WeWork (although they claim to not be coworking anymore).
 These offers have reassured businesses, even if we do not necessarily find the spirit of historic coworking spaces there anymore. On the other hand, we have to understand that when one teleworks only one day a week, he/she will prefer teleworking from home. Once weekly duration increases, the need to leave one’s home or not to be isolated, often manifests.
These offers have reassured businesses, even if we do not necessarily find the spirit of historic coworking spaces there anymore. On the other hand, we have to understand that when one teleworks only one day a week, he/she will prefer teleworking from home. Once weekly duration increases, the need to leave one’s home or not to be isolated, often manifests.
Can you mention some other examples of companies doing the same or dealing with another approach?
Corpoworking is not a very massive phenomenon. In France, we can mention SNCF or Orange, among the most famous companies to have adopted it. In Switzerland, I would mention examples such as SIG, BrainGym or Swisscom. In Germany, Modul57, TUI, AppHaus or SAP.
It seems companies are still reluctant to let their employees work out of third parties coworking spaces. Is this the case? Why?
That’s true, indeed, for France. Some companies fear that giving their employees space in coworking spaces creates a double cost: one for the office and another for the coworking space. However, the right solution would be to think about the flexibility of the company in a global way by integrating telecommuting, improving office spaces and using coworking spaces. One only has to look at the dramatic transformation of the Belgian social security, for instance, which introduced flex-office and teleworking in order to increase people’s productivity, motivation and quality of life… And it ultimately worked.
Does it start because of a change in companies’ culture or because of the growth of the coworking offering?
 I would say both. Without understanding the coworking phenomenon, a company is unlikely to let its employees work outside their offices. But coworking is becoming more and more successful, probably because it gives real estate businesses flexibility. And without sufficient supply of space, no access to coworking is possible.
I would say both. Without understanding the coworking phenomenon, a company is unlikely to let its employees work outside their offices. But coworking is becoming more and more successful, probably because it gives real estate businesses flexibility. And without sufficient supply of space, no access to coworking is possible.
Do you see the coworking offering in France improving to host companies’ employees, fitting needs in size, locations and amenities?
Nowadays, yes. In bigger cities, at least, all coworking spaces are well attended, and there are also spaces in more rural areas. In France there are 1,800 spaces (all types of third-places included). That’s a very fast progression. And the quality improves. We see that companies are using them more and more. It’s no longer about flexible workstation rentals, only. Coworking also becomes a natural solution to host temporary project teams for example. In that case, the objective is to put them calmly outside the company environment and confront them with diversity. For that reason, you see more and more tools coming up, such as creativity rooms, within coworking spaces.
What is missing?
Time to convert companies to this mode of management.
Speaking about geography, do you notice big differences in terms of behavior between Paris, on the on hand and the rest of France on the other hand?

Image source: Mutinerie Village, Coworking in the French Countryside. Copass SAS
The difference in behavior is more between the city and the countryside than between Paris and other cities in the province. The economic model of the urban spaces is viable because one can reach the minimum size for a correct profitability, around 1500/2000 m2. In rural areas, the smaller size of spaces, linked to a lower population density, makes breaking even difficult.
Who are the drivers of change (players) in France in the new ways of work? What excites you? What disappoints you?
There are many innovators in the new forms of work. One could even say that this innovation is a characteristic of third places. To name a few, I will mention Neo-Nomade, a platform that connects researchers and the suppliers of workspaces. They have a very fine knowledge of the market and are one of the important players who have changed the clientele of coworking spaces to a professional audience. I also want to mention Bureaux à partager, which is growing strongly in major French cities. Among other things, they have acquired a good know-how to install pop-up coworkings. We can also mention Now coworking who chose a high-end positioning with lots of activities offered – similar to the WeWork model but maintaining a stronger culture of community.
Their ambition is to open at least a dozen places in major French cities, outside Paris, in mythical places. Startway’s strategy is also interesting. It is that their spaces have a strong “entrepreneurship” orientation, with a lot of activities for the members. La Poste has entered into their capital and accelerated their development.
Finally, on the side of the spaces that are more “third-places” than coworking we can say that each large or medium city has one. I will mention Darwin in Bordeaux, the WIP being developed in Caen or The Station in the old station of Saint-Omer (14000 inhabitants).
How far do you see the workforce to be physically distributed in the coming 5 years time?
Difficult to know but if we look at strong trends, in France or elsewhere, it is likely that freelancers will be much more numerous than today. We are talking about 50% of the active population in the United States by 2030. It means a lot of flexibility, freedom in the choice of places to live and a greater need to freely recreate collective work in coworking spaces.
Some international studies claim flexible workplace will represent 30+% of the whole office market. Are we heading toward that direction?
In addition to the rise of freelancers phenomenon, we must add the demand for real estate flexibility from major rental companies. They no longer want the rigidity of conventional leases of 3-6-9 years and negotiate to get about 20% of space in flexibility. And who can better offer that than a coworking space?
Join us at Coworking Europe Conference for more insights, data and connections!


